Fiducial markers, often referred to simply as fiducials, play a crucial role in various scientific, medical, and industrial applications. These small objects or marks are strategically placed in an environment to serve as reference points or indicators. By understanding their fundamental purpose and diverse applications, one can appreciate the significant impact fiducial markers have on precision and accuracy across different fields.
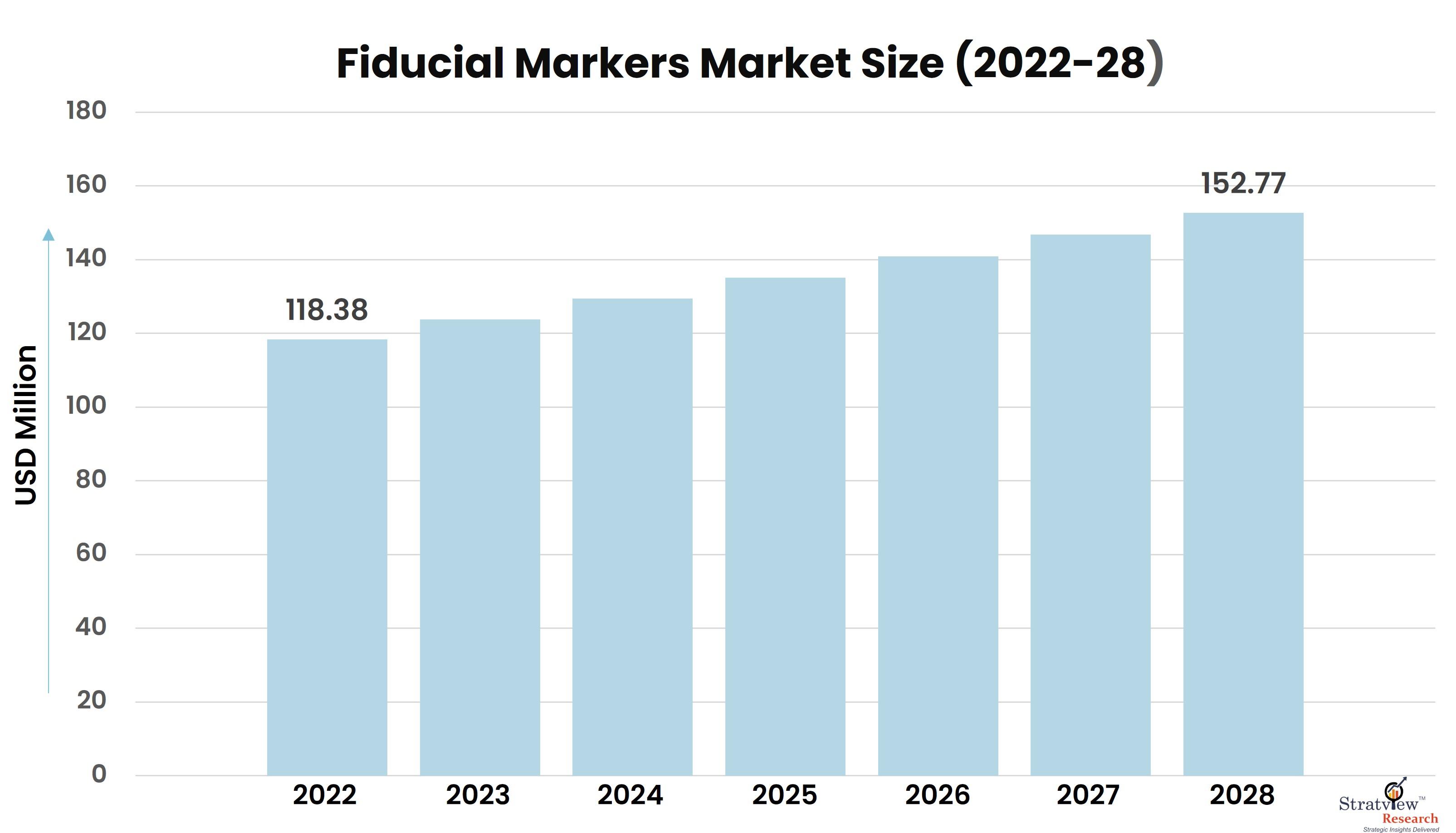
According to Stratview Research, the fiducial markers market was estimated at USD 118.38 million in 2022 and is likely to grow at a CAGR of 4.28% during 2023-2028 to reach USD 152.77 million in 2028.
What is a Fiducial Marker?
A fiducial marker is a medical device that is mainly placed on the object or body so that it can mark the area that needs surgery. These markers are very tiny equipment of the size of rice grains, which can help to target cancerous tumours or tissues without affecting the healthy ones. This device enables to mark off the exact position of the tumour and can help the doctor to provide maximum radiation dose to the particular area consisting of the tumour without harming the surrounding tissues.
Types of Fiducial Markers
Fiducial markers come in various forms, including:
Physical Markers: These are tangible objects placed in specific locations. Examples include small metal balls, reflective stickers, or specially designed shapes used in industrial settings.
Image-Based Markers: These markers are often used in digital imaging and computer vision applications. They are usually printed patterns or symbols that can be easily recognized by software algorithms.
Radiopaque Markers: Used primarily in medical imaging, these markers are made from materials that are visible under X-ray or other imaging modalities, helping radiologists and surgeons accurately identify specific locations within the body.
Applications of Fiducial Markers
Fiducial markers are integral to a wide range of applications, including:
Medical Imaging and Radiation Therapy: In medical imaging, fiducial markers are used to align images from different modalities (e.g., CT, MRI) or different time points. In radiation therapy, these markers help in precisely targeting tumors, ensuring that the radiation dose is accurately delivered to the intended area while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
Surgical Navigation: During surgical procedures, fiducial markers assist surgeons in accurately navigating instruments and implants, particularly in minimally invasive surgeries. These markers provide real-time feedback, enhancing the precision and safety of the procedures.
Robotics and Automation: In robotics, fiducial markers are used for localization and navigation. They enable robots to understand their position and orientation within an environment, facilitating tasks such as object manipulation and autonomous movement.
Augmented Reality (AR): Fiducial markers are used to overlay digital information onto the real world. By recognizing these markers, AR systems can accurately position virtual objects in the user's view, enhancing the immersive experience.
Importance of Fiducial Markers
The precision and accuracy provided by fiducial markers are critical in applications where even minor errors can have significant consequences. In medical procedures, for instance, the precise targeting enabled by fiducial markers can mean the difference between successful treatment and complications. In industrial automation, accurate localization can improve efficiency and reduce errors in manufacturing processes.
Conclusion
Fiducial markers, though small and often overlooked, are fundamental tools that enhance precision and accuracy in various fields. From medical imaging and surgery to robotics and augmented reality, these markers provide essential reference points that facilitate accurate measurements, alignments, and navigation. As technology continues to advance, the role of fiducial markers will likely expand, further underscoring their importance in achieving precision in diverse applications.