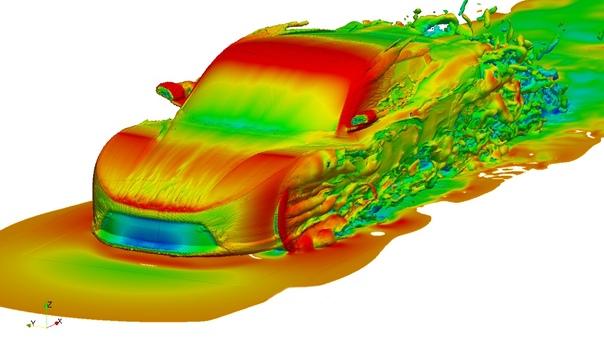
Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is a branch of fluid mechanics that uses numerical analysis and data structures to analyze and solve problems that involve fluid flows. The analysis of fluid flow by means of CFD encompasses the solution of the discretized equations governing the flow using techniques such as control volume method, finite element method (FEM) or finite difference method (FDM) on models that represent the geometry of a complex flow problem. The flow variables as well as other dependent properties like turbulent viscosity, skin friction, heat transfer etc. are computed and tabulated using the solved equations for further analysis of the flow.
Flow Phenomena Simulation using CFD
CFD is fundamentally based on the Navier-Stokes equations which mathematically describe the motion of viscous fluid substances. These equations can predict fluid flow, heat and mass transfer, chemical reactions and related phenomena. CFD found its extensive use in a diverse range of industrial applications since it permits modeling of complex fluid flow problems without extensive experimental validation. Some common examples where CFD simulation has become an integral part include aerodynamic analysis of aircraft and cars, cooling of electronic devices, fluid machinery design, chemical processing equipment, combustion applications, biomedical devices, environmental and weather modeling.
Methodologies used in CFD
There are three main categories of methodologies used for solving the equations in CFD - finite difference method (FDM), finite volume method (FVM) and finite element method (FEM).
FDM involves discretizing the equations on a structured mesh using finite differences to approximate the derivatives. It is accurate and relatively simple to implement but cannot handle complex geometries very well.
FVM subdivides the domain into finite control volumes and integrates the conserved quantities like mass, momentum, energy etc. over each control volume. It is extensively applied in Computational fluid dynamics as it conserves fluxes across control volume faces.
FEM discretizes the domain into interconnected elements and solves the weak form of the equations using interpolation functions. It provides flexibility to handle complex geometries but is computationally expensive compared to FDM and FVM.
Today, commercial CFD software heavily relies on unstructured grid techniques using cell-centered finite volume discretization for its robustness and ability to handle complex 3D problems.
Validation and Verification in CFD
Quality assurance and code assessment are crucial aspects of the CFD methodology. Validation is the process of determining the degree to which a CFD model accurately represents the real-world system being modeled. Verification ensures that the mathematical model and numerical method has been correctly implemented in the CFD code. This involves grid independence tests, residual monitoring, comparison with analytical solutions for simplified problems. Validation is performed by comparing the numerical predictions against well-established experimental data sets. Benchmarks cases are solved to establish confidence in using the code for new applications. Continuous efforts are required to achieve a good balance betweengrid resolution, turbulence treatment and overall accuracy.
Applications of CFD
Aerodynamics - Aircraft and automotive design involves extensive use of CFD for external aerodynamics analysis under different flow conditions. Internal flows like engines can also be modeled.
Combustion - CFD models permit detailed studies of combustion processes in engines, burners, furnaces by solving species transport and reaction kinetics. Ignition, pollutant formation etc. can be effectively captured.
Fluid Machinery - Pumps, turbines, compressors constitute critical equipment where flow behavior has to modeled using CFD to improve performance and minimize losses.
Heat Transfer - Computation of heat transfer coefficients, temperature distribution finds application in cooling of electronic equipment, heat exchangers, nuclear reactors and others.
Environment and Weather - Large eddy simulation (LES) techniques applied in CFD help understand meteorological phenomena like dispersion, turbulent mixing at microscopic level.
Biomedical - Blood flow in arteries, drug delivery analysis utilizes CFD tools due to the geometric complexity involved.
Computational fluid dynamics has revolutionized the process of fluid flow and heat transfer analysis in industrial and research environments. Its ability to provide detailed insights into complex flow problems without extensive experimental modeling has led to widespread adoption of CFD in all engineering domains. Continuous improvements in modeling techniques, high performance computing are increasing the reliability and application scope of CFD simulations. It has become an indispensable methodology complementary to theoretical and experimental methods.
the language that resonates with you
Get More Insights On Computational Fluid Dynamics
About Author:
Alice Mutum is a seasoned senior content editor at Coherent Market Insights, leveraging extensive expertise gained from her previous role as a content writer. With seven years in content development, Alice masterfully employs SEO best practices and cutting-edge digital marketing strategies to craft high-ranking, impactful content. As an editor, she meticulously ensures flawless grammar and punctuation, precise data accuracy, and perfect alignment with audience needs in every research report. Alice's dedication to excellence and her strategic approach to content make her an invaluable asset in the world of market insights.
(LinkedIn: www.linkedin.com/in/alice-mutum-3b247b137 )