Caring for a cat with diabetes can be a challenging journey, but with the right information and proper medical support, it is entirely manageable. One of the most common and effective treatments for feline diabetes is insulin therapy. Understanding how insulin for cats works, how it should be administered, and what pet owners should monitor can make a significant difference in a diabetic cat’s quality of life.
What Is Feline Diabetes?
Feline diabetes, or diabetes mellitus, occurs when a cat’s body cannot produce enough insulin or becomes resistant to it. Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar (glucose) levels. Without proper insulin function, a cat's blood sugar levels can become dangerously high, leading to symptoms such as excessive thirst, frequent urination, weight loss, increased appetite, and lethargy.
How Insulin Works for Cats
Insulin injections help regulate a diabetic cat’s blood glucose levels by mimicking the natural hormone produced by the pancreas. There are several types of insulin used in veterinary medicine, including short-acting, intermediate-acting, and long-acting formulas. The type of insulin prescribed depends on the cat's individual needs and how their body responds to treatment.
Most cats with diabetes will require twice-daily insulin injections, administered under the skin. Though the idea of giving injections can be intimidating for pet owners at first, it quickly becomes a routine task with practice and guidance from a veterinarian.
Choosing the Right Insulin
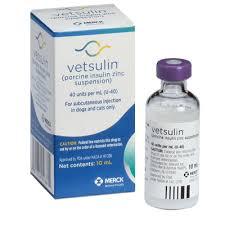
Veterinarians may prescribe human insulin products such as glargine (Lantus) or veterinary-specific options like Prozinc or Vetsulin. Each type has different onset times, durations, and dosing requirements. Your vet will determine the best insulin based on your cat’s condition, weight, and response to treatment. It's important never to switch insulin types or adjust doses without veterinary advice.
Monitoring Your Cat's Health
In addition to administering insulin, monitoring is key. Blood glucose levels should be regularly checked, either at home using a glucometer or through vet visits. Monitoring helps ensure that the insulin dose is effective and reduces the risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), which can be dangerous. Symptoms of hypoglycemia include weakness, confusion, tremors, and seizures—emergency care is essential if any of these signs occur.
Diet and exercise also play crucial roles in managing feline diabetes. A high-protein, low-carbohydrate diet is often recommended to help stabilize blood sugar levels. Maintaining a consistent feeding and insulin schedule is also vital.
Where to Find Insulin and Supplies
Reliable access to insulin and diabetic supplies is essential for ongoing treatment. Reputable online sources like petworldgdl.com offer various insulin options and diabetic supplies for cats, often at more affordable prices than traditional pharmacies.
Final Thoughts
With consistent care, many cats with diabetes can live happy, healthy lives. Insulin is a cornerstone of treatment, and while it requires commitment, the rewards are immense. Regular veterinary check-ups, diligent home monitoring, and a loving, informed approach to care make all the difference in managing your cat’s diabetes effectively.