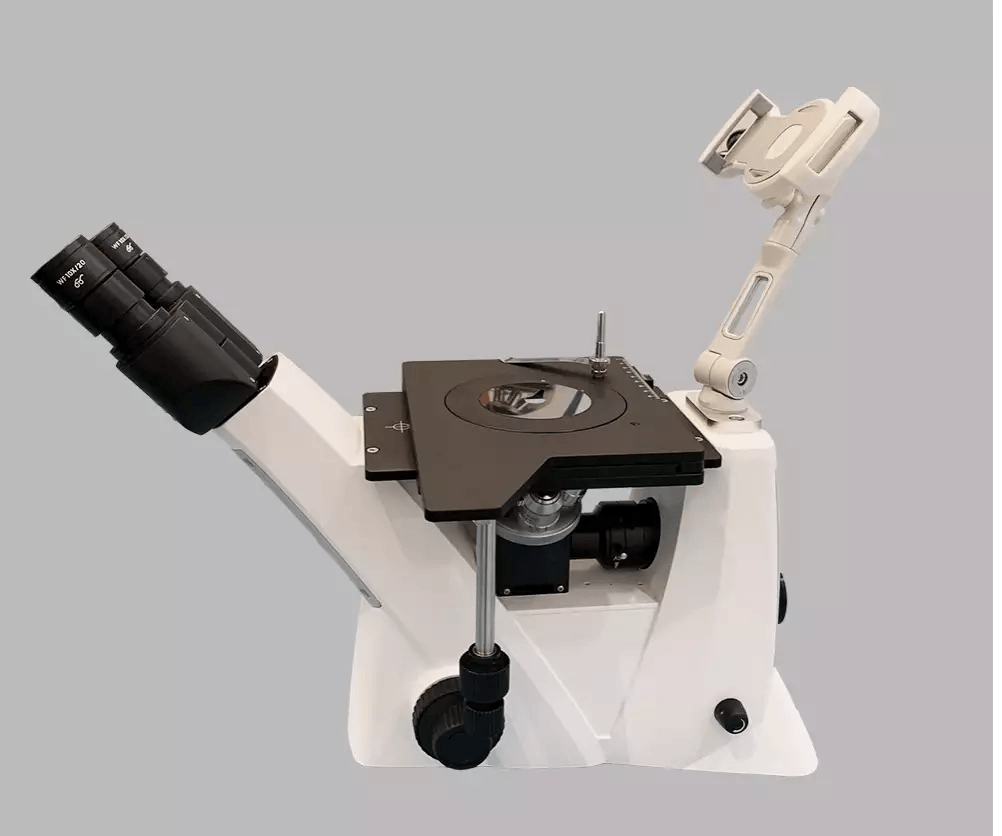
Metallurgical microscopes can be classified into two main types: upright and inverted.
Upright metallurgical microscopes are the most common type. The objective lenses are located above the stage, and the light source is located below the stage. In general, upright metallurgical microscopes cost less and require less training to use than inverted ones. They have a smaller field of view than inverted metallurgical microscopes.
Inverted metallurgical microscopes have objective lenses located below the stage, and the light source is located above the stage. Metallurgical inverted microscopes offer a larger field of vision and are more comfortable to use for extended periods of time, albeit frequently costing more than upright versions. Inverted metallurgical microscopes are also better suited for large-sample viewing.
In addition to upright and inverted metallurgical microscopes, there are also a number of specialized types of metallurgical microscopes, such as:
- Stereo metallurgical microscopes: The sample is visible with stereo metallurgical microscopes in three dimensions. They are mostly used for inspecting samples at low magnification.
- Digital metallurgical microscopes: A digital camera positioned on the eyepiece is a feature of digital metallurgical microscopes. By doing this, the user can view the sample on a computer screen and snap images of it.
- Polarizing metallurgical microscopes: Polarizing filters are used with metallurgical microscopes to analyze the crystal structure of metals. In research and development, they are commonly used.
Your unique needs will determine the ideal kind of metallurgical microscope for you. An upright metallurgical microscope is a suitable option if you need a general-purpose metallurgical microscope. If you need a metallurgical microscope with a large field of view or if you need to see large samples, an inverted metallurgical microscope is a good choice. A polarizing metallurgical microscope is a great option if you need to see the crystal structure of metals. A digital metallurgical microscope is a great tool for taking photographs of your materials.