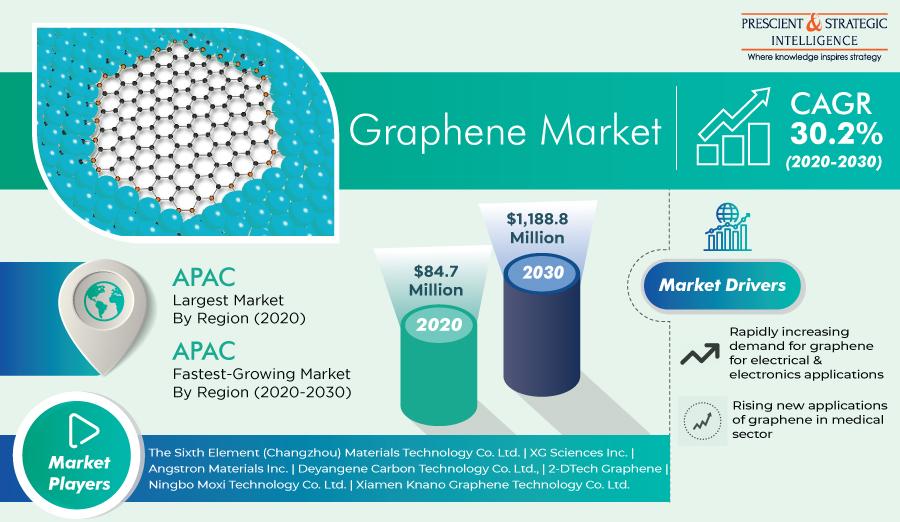
Introduction
Graphene, often hailed as a "wonder material," has captured the imagination of scientists, engineers, and innovators worldwide. With its exceptional properties and versatile applications, graphene holds the promise of revolutionizing numerous industries, from electronics and energy to healthcare and aerospace. This article offers a comprehensive overview of the graphene market, shedding light on its growth trajectory, emerging trends, and transformative potential.
Harnessing the Power of Graphene: Applications and Innovations
Electronics and Semiconductor Industry
In the realm of electronics and semiconductors, graphene's remarkable conductivity, flexibility, and transparency have sparked a wave of innovation. Graphene-based materials are paving the way for faster, more efficient electronic devices, including high-speed transistors, flexible displays, and ultra-sensitive sensors, revolutionizing the way we interact with technology and unlocking new possibilities for wearable devices and Internet of Things (IoT) applications.
Energy Storage and Renewable Energy
Graphene's lightweight and high surface area make it an ideal candidate for energy storage and renewable energy applications. Graphene-enhanced batteries, supercapacitors, and fuel cells offer enhanced energy density, faster charging rates, and improved cycle life compared to traditional energy storage solutions, driving advancements in electric vehicles, grid-scale energy storage, and portable electronic devices while reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating climate change.
Overcoming Challenges: Commercialization and Scalability
Production Scale-Up
Despite its remarkable properties, the widespread commercialization of graphene has been hindered by challenges related to production scalability, cost-effectiveness, and quality control. Developing scalable and cost-efficient manufacturing processes, such as chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and liquid-phase exfoliation, is crucial for unlocking the full potential of graphene and enabling mass adoption across various industries.
Regulatory Hurdles and Safety Concerns
The regulatory landscape surrounding graphene and graphene-based products remains complex, with uncertainties regarding health and environmental impacts. Addressing safety concerns, conducting rigorous risk assessments, and establishing standardized testing protocols are essential steps for ensuring the safe and responsible deployment of graphene technologies and gaining regulatory approval for commercial applications.
Embracing the Future: Key Trends and Opportunities in the Graphene Market
Advanced Materials and Composites
As research into graphene and its derivatives continues to advance, there is immense potential for the development of novel materials and composites with tailored properties and functionalities. Graphene-based nanocomposites, coatings, and membranes offer superior strength, conductivity, and barrier properties, opening up new opportunities in aerospace, automotive, construction, and protective coatings industries.
Biomedical and Healthcare Applications
In the field of biomedicine and healthcare, graphene holds promise for a wide range of applications, including drug delivery, tissue engineering, biosensing, and medical imaging. Graphene-based nanomaterials exhibit biocompatibility, antibacterial properties, and excellent mechanical strength, making them ideal candidates for next-generation medical devices, diagnostic tools, and therapeutics, revolutionizing patient care and disease management.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
How is graphene produced? Graphene can be produced through various methods, including mechanical exfoliation, chemical vapor deposition (CVD), and liquid-phase exfoliation, each offering unique advantages and challenges in terms of scalability, quality, and cost-effectiveness.
What are the key properties of graphene? Graphene is characterized by its exceptional strength, conductivity, flexibility, and transparency, making it an ideal material for a wide range of applications in electronics, energy storage, aerospace, and healthcare.
What are the environmental benefits of graphene? Graphene-based materials offer environmental benefits, including energy efficiency, resource conservation, and pollution reduction, by enabling the development of sustainable technologies, such as lightweight vehicles, efficient energy storage systems, and water purification membranes.
How does graphene contribute to technological innovation? Graphene's unique properties enable technological innovation across various industries, driving advancements in electronics, energy, healthcare, and materials science, and unlocking new opportunities for efficiency, performance, and sustainability.
What challenges are associated with graphene commercialization? Graphene commercialization faces challenges related to production scalability, cost-effectiveness, regulatory compliance, and safety concerns, requiring collaborative efforts from industry stakeholders, policymakers, and researchers to overcome.
What role does graphene play in the transition to a sustainable future? Graphene plays a crucial role in the transition to a sustainable future by enabling the development of clean energy technologies, lightweight and fuel-efficient vehicles, and advanced materials with minimal environmental impact, contributing to global efforts to address climate change and resource depletion.