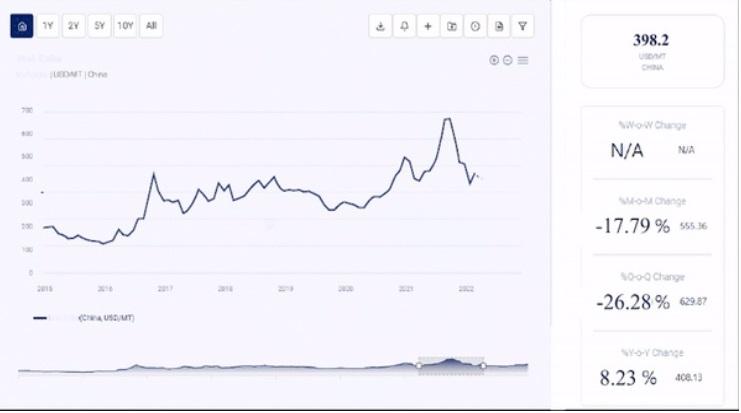
In today's rapidly evolving global landscape, understanding the intricate dynamics of land cost prices is paramount for investors, developers, and policymakers alike. As the demand for land continues to surge across various regions, staying abreast of the latest insights on price movement and trend analysis is crucial. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the nuances of land cost prices, examining trends and forecasts across different regions worldwide, including Asia, Europe, North America, Latin America, and the Middle East & Africa.
Request for Real-Time Land Cost Prices: https://www.procurementresource.com/resource-center/land-cost-price-trends/pricerequest
Definition of Land Cost:
Land cost refers to the monetary value associated with acquiring or owning a piece of land. It encompasses various factors such as location, size, zoning regulations, infrastructure availability, and market demand. Essentially, it represents the initial investment required to secure land for development or investment purposes.
Key Details About Land Cost Price Trend:
Land cost prices are subject to fluctuation due to numerous factors influencing supply and demand dynamics. Understanding these trends is crucial for making informed decisions in real estate and land development ventures. Here are some key details about land cost price trend:
-
Economic Factors: Economic conditions play a significant role in shaping land cost prices. Factors such as GDP growth, inflation rates, interest rates, and unemployment levels can influence the overall demand for land and subsequently impact its price.
-
Urbanization and Population Growth: Rapid urbanization and population growth exert pressure on available land resources, driving up land prices in urban and suburban areas. Regions experiencing significant demographic shifts often witness escalating land costs due to increased demand for residential, commercial, and industrial developments.
-
Infrastructure Development: Infrastructure projects, such as transportation networks, utilities, and amenities, can significantly enhance the value of land in their proximity. Areas undergoing infrastructure development tend to attract investments, leading to appreciation in land prices.
-
Regulatory Policies: Zoning regulations, land use restrictions, and government policies regarding land ownership and development can have a profound impact on land cost prices. Changes in regulatory frameworks can either stimulate or dampen land market activity, influencing price trends accordingly.
Industrial Uses Impacting Land Cost Price Trend:
The industrial sector plays a pivotal role in shaping land cost prices, particularly in regions with thriving manufacturing, logistics, and warehousing activities. Here are some industrial uses that impact land cost price trends:
-
Manufacturing Hubs: Regions with established manufacturing hubs often experience heightened demand for industrial land, driving up prices. Proximity to transportation networks and access to skilled labor are key determinants of land values in manufacturing-intensive areas.
-
Logistics and Distribution Centers: With the rise of e-commerce and global trade, the demand for logistics and distribution centers has surged. Land located near major transportation hubs, ports, and airports commands premium prices due to its strategic importance in supply chain operations.
-
Technology and Innovation Clusters: Technology parks, research institutions, and innovation clusters attract investments from tech companies and startups, driving up land prices in these areas. Access to talent, intellectual property, and collaborative opportunities contributes to the appreciation of land values.
Key Players:
Several stakeholders influence land cost prices, ranging from individual landowners to institutional investors and real estate developers. Understanding the roles of these key players is essential for navigating the complexities of the land market:
-
Developers and Investors: Real estate developers and investors play a pivotal role in driving demand for land by initiating development projects and acquiring land for future ventures. Their investment decisions and market strategies directly impact land cost prices.
-
Government Agencies: Regulatory bodies and government agencies influence land cost prices through zoning regulations, land-use policies, taxation measures, and infrastructure investments. Their interventions shape the overall landscape of the land market.
-
Landowners and Sellers: Individual landowners, corporations, and institutional investors looking to monetize their land assets contribute to the supply side of the land market. Their pricing decisions and willingness to sell influence market dynamics and price trends.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, navigating the complexities of land cost prices requires a comprehensive understanding of market dynamics, trends, and key influencers. As global economic, demographic, and industrial shifts continue to shape the land market, staying informed about price movements and forecasts is essential for successful procurement and investment decisions. Whether acquiring land for residential, commercial, or industrial purposes, leveraging insights into land cost trends can optimize procurement resource and maximize investment returns. By monitoring regional trends, analyzing industrial impacts, and engaging with key players in the land market, stakeholders can position themselves strategically to capitalize on opportunities and mitigate risks in an ever-evolving landscape.